6TH OF APRIL 2021



THE CONCEPT IDEA IS TO ENHANCE THE PORT OF TRIPOLI IN ORDER TO ENTERTAIN AND ATTRACT MORE PEOPLE TO VISIT THIS PART OF LEBANON.
CREATING CORNERS FOR PLAY GROUNDS AROUND THE DOCK AREA TO MAKE IT MORE ALIVE WITH CONTAINER THEMED RESTAURANTS SO THAT PEOPLE CAN GATHER.
MOREOVER, BOUTIQUE HOTELS COULD ALSO BE PART OF THIS PROJECT SO IT CAN REVIVE THE AREA OF TRIPOLI WHICH LEADS TO A BOOST IN THE ECONOMY OF THE SECOND LARGEST POPULATION CITY IN LEBANON – TRIPOLI.
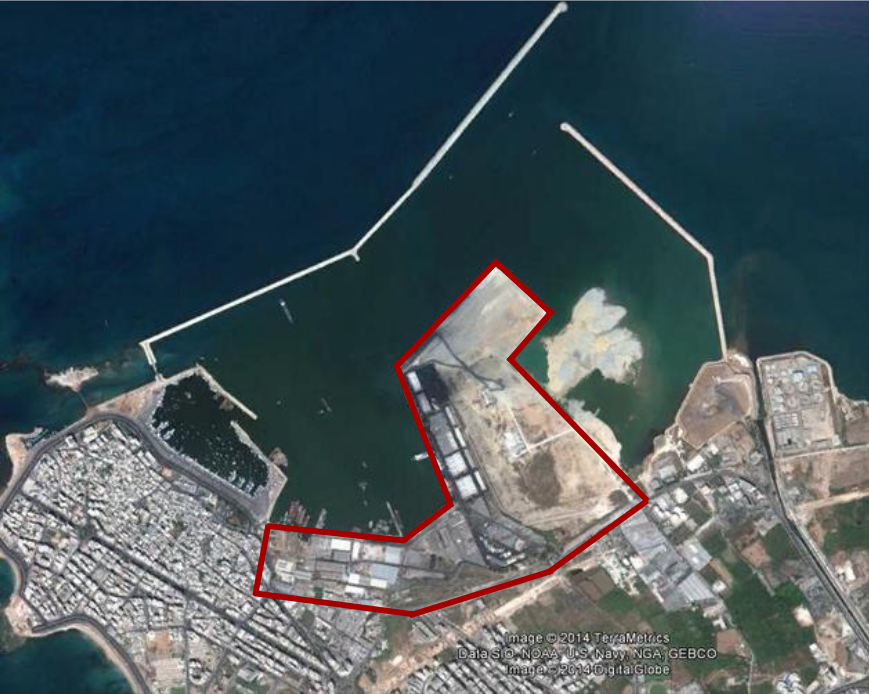
LOCATION
WHO WILL COLLABORATE WITH US

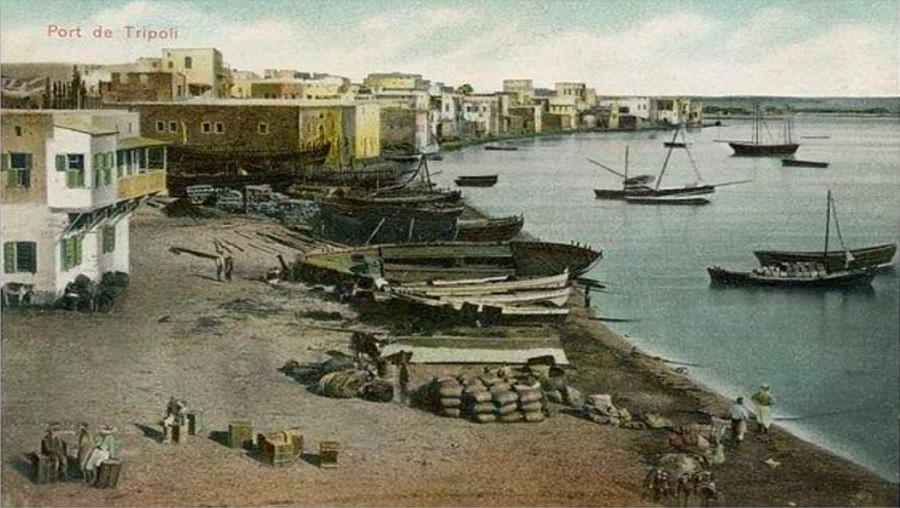
THE PORT OF TRIPOLI

The port of Tripoli remained by and large a nature formed harbor, a geographical strip of land where sailboats servicing the trade lines along the coastlines of Turkey, Syria, Lebanon and Egypt, extending to Malta, Crete and Greece would dock. The half moon shaped gulf of El Mina acted as natural shelter to North East winds that create strong currents in deep waters.
Ships docked in the El Mina gulf and were serviced by local merchant boats that would offload the ship cargo by manual labor to the small boats that would transfer the goods to the dry docks. Ships up to the early twentieth century remained small to medium loads of 50 to 75 tons per ship.
The first significant development came during the French Mandate when two dry docks , Gremblad and Sheikh Afan , were constructed to allow military tugboats to dock. A third and rarely used natural harbor on the east side of the city acted as backup when the North East winds were exceptionally strong, however the rocky nature of that area was a last resort and required the best of the local seamen's expertise, sometimes assisted by El Mina fisherman who knew the waters well.
At the dawn of the Second World War , French Fighter and Supply Planes coming from the Far East (India, China and Vietnam) used the El Mina basin as a landing area. Significantly lighter weight than sailboats, the local current within the basin caused problems and then El Mina Mayor Kheireddine Abdul Wahab was given the contract to construct the first man made break water which marked the beginning of the Tripoli Harbor.
Sailboats built mainly in Arwad island and later also in El Mina as well, had been in sharp decline with the rise of Steam Ships, and the city had seen increased activity as an offloading site for merchant ships, and with service industries emerging, such as the use of transport Barges which would be used to offload the ship's cargo from its anchored position to the sea shores The French Mandate continued its development of the port by constructing a small docking station within the man made pond resulting from the break water constructed and now buzzing with Barges. Barges would dock an allow for faster and more efficient cargo offloading and was transported to the railway station and on to the wagons into inland Syria, Iraq and Jordan. This also coincided with the Iraq Petroleum Company (IPC) pipeline project to import steel and iron for its refinery construction project in the neighbouring Lebanese town of Bedawi.
During the late 1950s, the government of Lebanese President Kamil Chamoun and Prime Minister Rashid Karami awarded a contract to the Italian company Veining to construct a modern day harbor. Intense lobbying from Beirut Harbor patrons, the depth of the inner harbor pond was restricted to 8 meters, which would later hinder the Tripoli harbor from receiving larger vessels. With work beginning in 1957, the first Board of Directors was appointed in 1961 to oversee the day to day operation of the harbor, now a government entity.
SERVICES AND FACILITIES
Ships docking on one of the port's quays
Warehouses & Yards
• 4 Warehouses for dry drainage goods, with an area of 11,000 m2 10 Warehouses for dry drainage goods and Wood, with an area of 17,500 m2
• 5 Yards to store vehicles, with an area exceeding 10,000 m2
• 1 Yard to store Containers, with an area of 10,000 m2
• 1 Yard for general purpose, with an area of 15,000 m2
• 2 Yards with an area of 3,000 m2 to store fir wood
Port Equipment
• 6 Mobile cranes with capacity of 125–165 tons
• 7 Mobile cranes with capacity of 100–120 tons
• 10 Mobile cranes with capacity of 70–90 tons
• 20 Mobile cranes with capacity of 40–65 tons
• 11 Mobile cranes with capacity of 25–38 tons
• 15 gafs for drainage goods
• 24 Forklifts
• 8 Bulldozers
• 30 Trucks
• 4 Tractors
Equipment for stowage of dry drainage goods
• Water Supply
• 8 outlets to supply ships with water using modern technologies
• A shalon with a reservoir to supply ships with water inside and outside the basins (this service is provided by the guidance station) Other Services
• 3 Cafeterias to serve the Administration building and the Berths
• A Hospital (under construction)
• An office for the Workers' Union

CONTAINER THEMED RESTAURANTS

COLORFUL GEOMETRIC PATTERNS





























